Apache is one of the most widely used web server software applications in the world. A W3Techs survey estimates that just over 31 percent of all known web servers use a version of Apache. It’s highly customizable, responsive, and completely open-source.
Apache is an excellent and well-established option for running a website. It’s vital to know how to do essential maintenance when running an Apache web server. Here are five different ways to check your Apache server status on Linux.

1. Check Web Server Status With apachectl
The simplest method to check your Apache web server’s status involves theapachectlcommand. All you need to do is enter:
If your Apache server is up and running, the terminal will output information like your server uptime and the number of total requests that it has received. Alternatively, you may receive error info for an active but misconfigured Apache server.
2. Check Apache Server Status With mod_status
You can view more information about your Apache web server by enabling mod_status. Once this module is enabled, you’ll be able to visit a page athttp://localhostto view information about your server.
Enable Apache server-status
you’re able to enableserver-statuswith just a few commands, depending on your Linux distribution. If you’re using Ubuntu, open the/mods-enabled/status.confconfiguration file to check whether server-status is enabled:
Edit the<Location /server-status>section of the file as shown in the following lines to enable generating server status reports from your IP address:
Finally, save and exit the file. You’ll need to restart the Apache service before your changes take effect:
If you have a classic Linux system that uses SysVinit, you may need touse service instead of systemctl. Make this substitution for any other systemctl commands listed!
When using RHEL and Fedora, you will need to use a slightly different method to enableserver-status. Enter the following to open the server-status configuration file:
Next, edit the<Location “/server-status”>section to use the same configuration as the following lines:
ensure to replaceYourIPAddressin the above text snippet with your IP address. Once done, save and exit the file. Finally,use systemctl to restart the serviceand your changes will take effect:
View Server Status in Your Browser
Checking your Apache server status is easy once you’ve entered all of the requisite commands to enable the mod_status module. You can view information about your web server by visiting http://localhost/server-status.
3. Use the ps Command to Check the Apache Status
you may also use theps (“process status”) utilityto check the status of your Apache web server. You can enter the following to select all active processes, specify the outputs you would like to view, and filter by “apache2”:
On RHEL and Fedora, refer tohttpdinstead ofapache2while using the above command. You’ll know that your Apache web server is running if the command returns an output. The command returns any process statuses mentioning apache2 from any users (a) with the process owner (u) and also includes any processes not associated with a terminal (x).
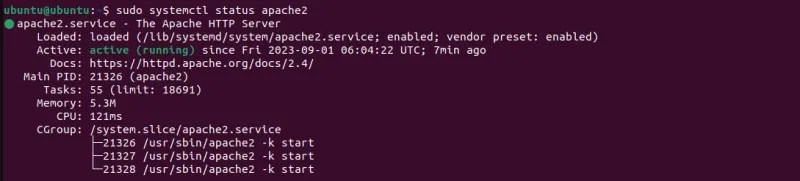
4. Check Apache Web Server Status With systemctl
Beyond its typical functions, you may also use systemctl to check the status of your Apache web server. You can essentially check whether any service started by systemd is still running with the right spin on a systemctl command.
On distributions such as Ubuntu and openSUSE, you can check whether your Apache web server is running with:
You’ll need to use a variant of this command on RHEL and Fedora, as Apache HTTP servers are handled by the httpd package. Enter the following to check the status of your web server:
Some users encounter the “Unit apache2.service could not be found” error after running this command. If you’re struggling to determine what service to refer to, you’re able to use the following command to browse through a list of your system services:
5. Check Apache Server Through Your Web Browser
You don’t have to bother with the mod_status module to do a basic check on your web server. Visiting the default localhost page is one of the most uncomplicated ways to check your Apache server status.
To check the server status through your web browser, enter http://localhost in your search bar.
If your Apache web server is up and running, you will see a test page that reads “It Works!” You maysee a page with error 403if your server is configured incorrectly—you’re able to troubleshoot this by checking/var/log/apache2/error_logfor more information.
Monitor Your Apache Server on Linux
Maintenance and monitoring are just two small parts of the complicated undertaking of running a web server. Reading official Apache documentation, looking for guides published by your Linux distribution, and even watching topical YouTube videos are all great ways for you to learn more about your web server and become a skilled webmaster.